Common Mistakes in Animal Cell Diagrams: Animal Cell Coloring Guide Answer Key
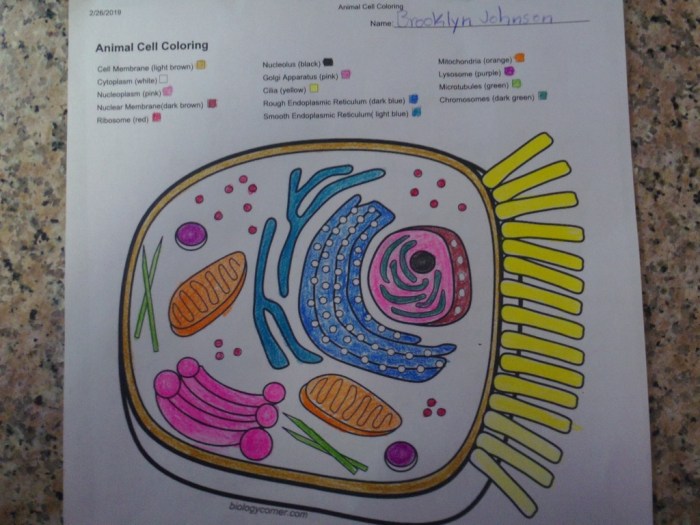
Animal cell coloring guide answer key – Creating accurate and informative animal cell diagrams is crucial for understanding cell biology. However, students often make common errors that can hinder their comprehension of cell structure and function. These mistakes often stem from a lack of precise understanding of the organelles and their relative sizes and positions within the cell. Addressing these errors early on can significantly improve learning outcomes.
Inaccurate depictions of animal cell components lead to misconceptions about their roles in cellular processes. For example, misrepresenting the size or shape of the nucleus can lead to a flawed understanding of its function as the control center of the cell. Similarly, incorrect placement or omission of organelles like the Golgi apparatus or mitochondria can result in an incomplete picture of cellular metabolism and protein trafficking.
Incorrect Representation of Organelle Shape and Size
Accurate representation of organelle shape and size is essential for a proper understanding of their function. Many students struggle to visualize the three-dimensional nature of these structures and often draw them in simplified, inaccurate forms. For instance, the endoplasmic reticulum is frequently depicted as a simple, smooth structure, ignoring its extensive network of interconnected membranes. The mitochondria, often depicted as simple ovals, are actually complex organelles with internal cristae.
This simplification obscures the critical role of these cristae in ATP production. To avoid these mistakes, students should consult multiple reliable sources, including textbooks and online resources with high-quality images, and practice drawing the organelles from various perspectives.
Mislabeling or Omission of Key Organelles
Another frequent error involves the mislabeling or complete omission of essential organelles. This significantly impacts the understanding of cellular processes. For example, mistaking the lysosome for a vacuole, or omitting the ribosomes entirely, can lead to significant misconceptions about cellular digestion and protein synthesis. Furthermore, incorrect labeling can confuse the function of the organelles, making it difficult to understand their interrelationships.
To mitigate this, systematic approaches to labeling are recommended. This includes referencing a reliable diagram and ensuring each organelle is clearly identified with its correct name and location.
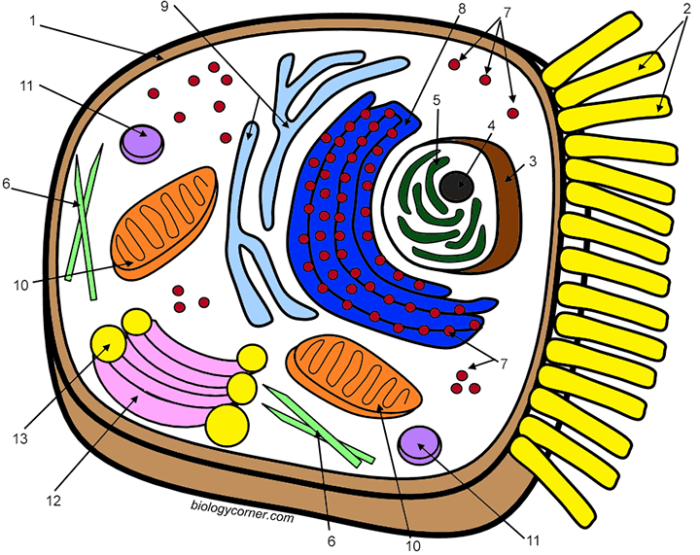
- Begin by drawing a basic Artikel of the cell membrane.
- Next, add the nucleus, ensuring it’s proportionally sized and centrally located.
- Then, add the other major organelles: mitochondria (depicting the cristae if possible), endoplasmic reticulum (showing both rough and smooth regions), Golgi apparatus (as a stack of flattened sacs), lysosomes (small, spherical), and ribosomes (small dots, potentially attached to the rough ER).
- Finally, carefully label each organelle using clear, concise labels and connecting lines.
Inconsistent Scale and Proportion
Maintaining consistent scale and proportion within the cell diagram is crucial for a realistic representation. Students often draw organelles disproportionately large or small relative to each other and the cell itself. For example, the nucleus might be drawn far too large compared to the cytoplasm, or the mitochondria might be drawn significantly smaller than they actually are. This lack of scale makes it difficult to appreciate the relative abundance and spatial arrangement of organelles within the cell.
Understanding the intricacies of an animal cell necessitates a thorough comprehension of its organelles, a process often aided by visual learning tools such as an animal cell coloring guide answer key. To enhance this understanding, supplementing the guide with practical activities like coloring can prove beneficial; readily available resources for this include printable coloring pages, such as those found at printing coloring pages of animals , which can provide a foundation for understanding animal morphology before delving into cellular structures.
Returning to the animal cell coloring guide answer key, its use in conjunction with these visual aids significantly improves comprehension and retention.
To avoid this, using a reference image with a scale bar is recommended, along with paying close attention to the relative sizes of organelles described in reliable sources.
Comparing Animal and Plant Cells
Animal and plant cells, while both eukaryotic, exhibit significant structural differences that reflect their distinct functions and lifestyles. Understanding these differences provides valuable insight into the diverse strategies employed by living organisms to thrive in their respective environments. This comparison will highlight key structural variations and their functional implications.
Both animal and plant cells share fundamental characteristics as eukaryotic cells. They both possess a nucleus containing genetic material, a cytoplasm filled with organelles, and a cell membrane that regulates the passage of substances. However, several key organelles distinguish one from the other, impacting their overall capabilities and survival strategies.
Organelle Presence and Absence, Animal cell coloring guide answer key
Plant cells possess several organelles not found in animal cells, while animal cells contain some structures absent in plant cells. This difference is directly related to their respective metabolic needs and ecological roles. The presence or absence of specific organelles directly impacts the functions each cell type can perform.
| Feature | Animal Cell | Plant Cell | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Absent | Present (composed of cellulose) | Plant cells have a rigid cell wall providing structural support and protection; animal cells lack this rigid outer layer, relying instead on their cytoskeleton for support. |
| Chloroplasts | Absent | Present (sites of photosynthesis) | Plant cells perform photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy; animal cells lack this capability and rely on consuming organic molecules for energy. |
| Large Central Vacuole | Absent or small | Present (maintains turgor pressure, stores water and nutrients) | The large central vacuole in plant cells plays a crucial role in maintaining cell shape and turgor pressure, while animal cells may have smaller vacuoles with different functions. |
| Plasmodesmata | Absent | Present (channels connecting adjacent cells) | Plant cells are interconnected through plasmodesmata, facilitating communication and transport between cells; animal cells lack these direct cytoplasmic connections. |
| Centrioles | Present (involved in cell division) | Usually absent | While animal cells utilize centrioles in cell division, plant cells typically use other mechanisms to organize microtubules during this process. |
Functional Implications of Structural Differences
The structural differences between animal and plant cells directly influence their respective functions. For example, the rigid cell wall of plant cells allows them to withstand significant osmotic pressure changes, a crucial adaptation for terrestrial life. The absence of a cell wall in animal cells allows for greater flexibility and motility, enabling diverse cell types and functions within complex multicellular organisms.
The chloroplasts in plant cells enable autotrophic nutrition, while animal cells, lacking chloroplasts, are heterotrophic, relying on external sources of organic molecules for energy. The large central vacuole in plant cells contributes to water regulation and storage, impacting their ability to survive periods of drought. In contrast, animal cells use diverse mechanisms for water balance and nutrient storage.
These structural variations are essential for the survival and functioning of each cell type in its unique environment.
Query Resolution
What are some good resources beyond this guide for learning about animal cells?
Textbooks, online educational videos, and interactive simulations are excellent supplementary resources.
Why is it important to use specific colors when coloring organelles?
Using specific colors helps in distinguishing organelles and improves memorization of their functions and locations.
Are there any online tools to help with creating animal cell diagrams?
Yes, several online tools offer templates and interactive features for creating and labeling cell diagrams.
How does understanding animal cells relate to medical research?
Understanding animal cells is crucial for researching diseases, developing treatments, and advancing biotechnology.



